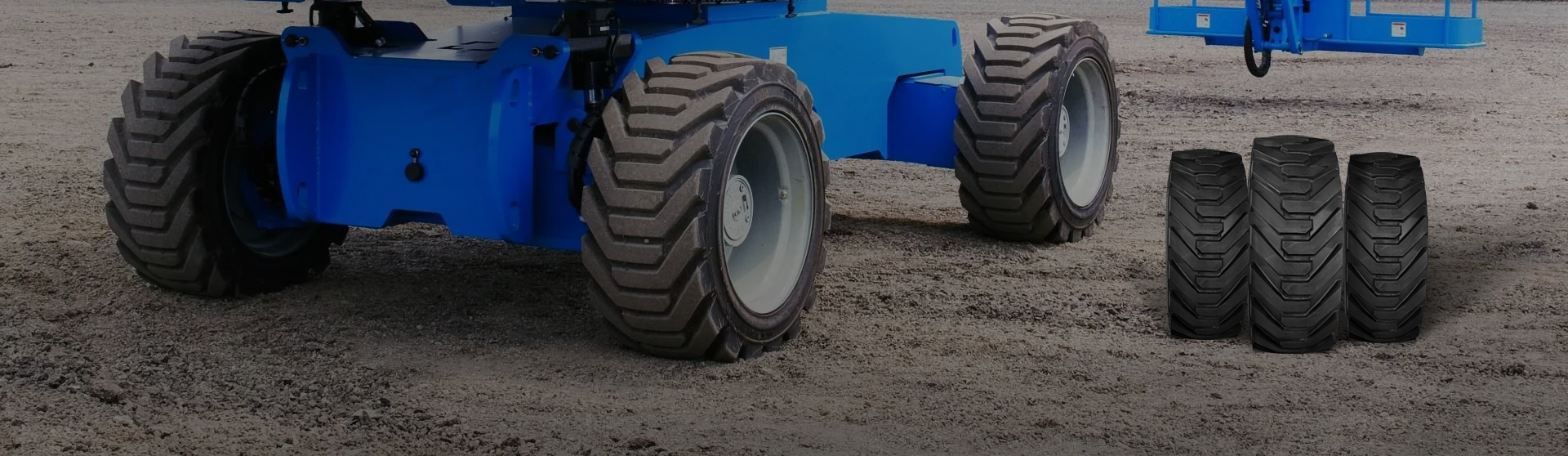
When choosing tires for equipment such as carts, machinery, and even vehicles, it’s important to consider the materials that make up the tire, as they can significantly affect performance, durability, and cost. Rubber Tires and Polyurethane Tires are two popular choices in the market, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific needs of the user. This article will compare Rubber Tires and Polyurethane Tires across several key factors, including performance, durability, cost, and applications in various industries like automotive, industrial machinery, and material handling.
What Are Rubber Tires?
Rubber Tires are the most traditional and widely used type of tires, commonly found in cars, trucks, bicycles, and various industrial equipment. These tires are made from natural or synthetic rubber compounds that offer flexibility, comfort, and traction. Rubber tires are designed to provide a smooth ride and can withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, making them a versatile choice for many applications, including heavy-duty vehicle tires and light-duty machinery tires.
Key Features of Rubber Tires:
-
Flexible and Comfortable: The natural elasticity of rubber allows the tire to absorb shocks and vibrations, providing a smooth and comfortable ride. This makes rubber tires for bicycles or vehicle tires for trucks a popular choice for road trips and city commutes.
-
Good Traction: Rubber tires excel at providing traction on different surfaces, from dry roads to wet and slippery conditions, making them perfect for all-weather vehicle tires.
-
Wide Availability: Rubber tires are used in various applications, from vehicles to industrial equipment, making them widely available and easy to replace in both automotive tire shops and machinery maintenance centers.
Common Applications:
-
Automotive Repairs: The most common application for rubber tires is in vehicles, where their ability to provide traction and comfort is essential.
-
Bicycles and Motorcycles: Rubber tires are used in two-wheeled vehicles, offering flexibility, grip, and shock absorption.
-
Industrial Equipment: Rubber tires are also used in heavy-duty machinery and carts, where flexibility and comfort are important.
What Are Polyurethane Tires?
Polyurethane Tires, also known as Polyurethane Rubber Tires, are made from a synthetic material called polyurethane, which offers higher durability and load-bearing capacity than rubber. Polyurethane tires are often used in applications where high resistance to wear, impact, and abrasion is required. These tires are solid, meaning they do not have air chambers, making them maintenance-free.
Key Features of Polyurethane Tires:
-
High Durability: Polyurethane tires are known for their resistance to wear, tear, and abrasion, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial tires and warehouse material handling. They’re the go-to choice for forklift tires and other heavy-duty machinery tires.
-
Non-Pneumatic: These tires do not require inflation, which eliminates the risk of punctures, flats, or leaks—making them ideal for industrial machinery that needs to run continuously without downtime.
-
Excellent Load-Bearing Capacity: Polyurethane tires can support heavier loads compared to rubber tires, making them suitable for industrial applications like forklift tires and material handling equipment.
Common Applications:
-
Warehouse Equipment: Polyurethane tires are commonly used in material handling equipment like forklifts, pallet jacks, and platform carts.
-
Industrial Machinery: Due to their durability, these tires are used in factory settings, particularly in heavy-duty machinery and automated systems.
-
Carts and Trolleys: Polyurethane tires are often found in carts used for transportation in industrial environments, as they offer superior longevity and puncture resistance.
Comparison Table: Rubber Tires vs. Polyurethane Tires
| Feature | Rubber Tires | Polyurethane Tires |
| Material | Natural or synthetic rubber | Polyurethane (a synthetic polymer) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and elastic, absorbs shocks | Less flexible, but offers more resistance to wear |
| Durability | Moderate, can wear out over time due to abrasion and punctures | High, excellent resistance to abrasion, cuts, and punctures |
| Comfort | High, absorbs vibrations and shocks effectively | Moderate, less shock absorption than rubber tires |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, suitable for standard applications | High, designed to handle heavy loads in industrial environments |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic maintenance, prone to punctures and flats | Maintenance-free, no risk of punctures or flats |
| Traction | Excellent grip on various surfaces (wet, dry, rough) | Good traction but may not perform as well on certain surfaces |
| Cost | Moderate, affordable depending on the application | Higher upfront cost but more cost-effective over time due to durability |
| Applications | Vehicles, bicycles, motorcycles, carts, machinery | Warehouse equipment, forklifts, industrial machinery, carts |
Pros and Cons of Each Type of Tire
Rubber Tires:
Pros:
-
Flexibility and Comfort: Rubber tires are designed to absorb shocks and vibrations, providing a smooth and comfortable ride for vehicles and bicycles.
-
Traction on Multiple Surfaces: Rubber tires excel in providing grip on a variety of surfaces, including wet, dry, and rough terrain, making them ideal for automobile tires.
-
Wide Availability: Rubber tires are ubiquitous, and finding replacements is easy and affordable across different tire repair shops.
-
Lower Initial Cost: Rubber tires tend to be cheaper upfront, especially for smaller applications like bicycles, light-duty vehicles, and casual carts.
Cons:
-
Wear and Tear: Rubber tires are prone to wear from constant use, especially on rough surfaces or under heavy loads, making them less durable for heavy-duty material handling.
-
Puncture Risk: Air-filled rubber tires are susceptible to punctures and flats, leading to more maintenance and downtime, particularly in industrial settings.
-
Less Durability: Rubber tires have a shorter lifespan compared to polyurethane tires, especially in harsh industrial environments where wear-resistant tires are essential.
Polyurethane Tires:
Pros:
-
High Durability: Polyurethane tires are highly resistant to wear, cuts, and abrasion, making them perfect for demanding environments such as material handling equipment and forklifts.
-
No Risk of Punctures: Since they are solid, polyurethane tires do not require inflation and are immune to punctures or flats, ideal for industrial machinery.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity: These tires can support significantly heavier loads than rubber tires, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial tires and warehouse carts.
-
Low Maintenance: These tires are maintenance-free, offering longevity and reducing downtime for replacements in warehouse operations and logistics equipment.
Cons:
-
Less Comfortable: Polyurethane tires do not absorb shocks as effectively as rubber tires, leading to a rougher ride. They are less suitable for bicycle tires or personal vehicles that require a smooth and comfortable ride.
-
Higher Initial Cost: The upfront cost of polyurethane tires is higher than rubber tires, especially for applications in high-duty industrial equipment.
-
Limited Traction on Certain Surfaces: While durable, polyurethane tires may not perform as well as rubber tires on wet, icy, or slippery surfaces, making them less ideal for automotive tires in adverse weather conditions.
Which Tire Should You Choose?
-
Choose Rubber Tires if: You need a flexible, comfortable, and cost-effective solution for applications that don’t require high load-bearing capacity or exposure to extreme wear and tear. Rubber tires for vehicles, bicycles, and light-duty machinery are ideal when comfort, traction, and affordability are the main priorities.
-
Choose Polyurethane Tires if: You are working in an industrial or heavy-duty environment where durability, load-bearing capacity, and maintenance-free operation are crucial. Polyurethane tires for forklifts, material handling equipment, and heavy-duty carts are the best choice when long-term durability and reduced maintenance are key.
Rubber Tires and Polyurethane Tires each have their strengths and ideal use cases. Rubber Tires are perfect for everyday use in automobiles, bicycles, and light-duty machinery, where comfort, traction, and affordability are the main factors. On the other hand, Polyurethane Tires are built for durability and high load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty machinery, warehouse equipment, and industrial applications where performance and minimal downtime are essential. By considering factors like cost, durability, and application, you can choose the best tire for your needs and ensure optimal performance for your equipment.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى